The Breed Standard of the Coton de Tulear
The main standard for the Coton de Tulear is the FCI standard as this is the only one officially approved and endorsed by the Coton de Tulear Club of Madagascar, the breeds country of origin.
It is also important to know that the FCI standard is the only standard recognised and followed worldwide. When showing your Coton abroad the Kennel Club standard of that country applies,it may differ from your own Kennel Club standard. Here we use the U.K. Kennel Club standard a much shorter breed standard which differs slightly from the F.C.I. standard.
Below is The Official Kennel Club Coton de Tulear Breed Standard of the United Kingdom in green, illustrated for the CDT Club of the United Kingdom by Jo Scott of Cukoton COTON DE TULEAR









The Federation Cynologique Internationale (F.C.I.) standard
FCI-Standard Number 283 - 25..04.1996 GB Translation: Mrs Peggy Davis
Date of publication of the valid original standard - 09.11.1995
The Coton de Tulear was recognised as a rare breed, in France in 1977. There utilization is a companion dog. Classification FCI: Group 9 companions and toys
General Appearance
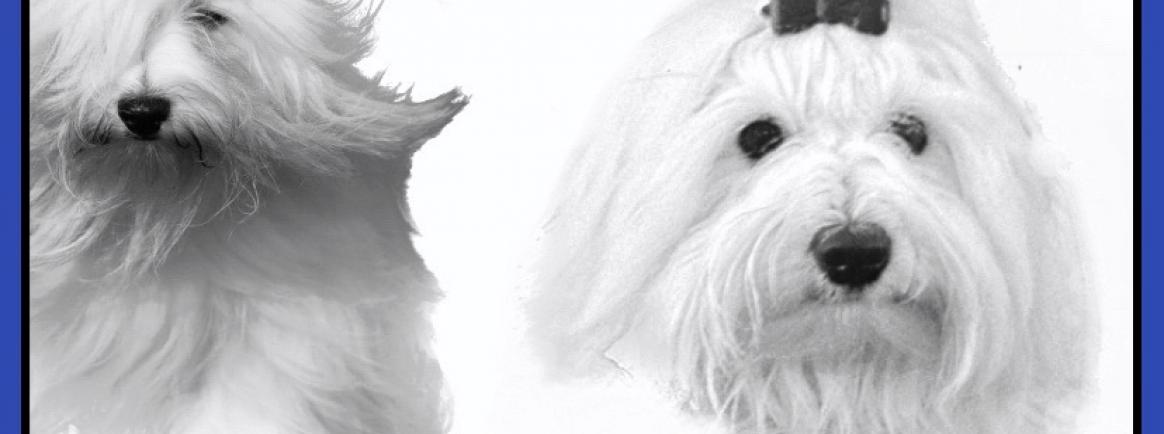
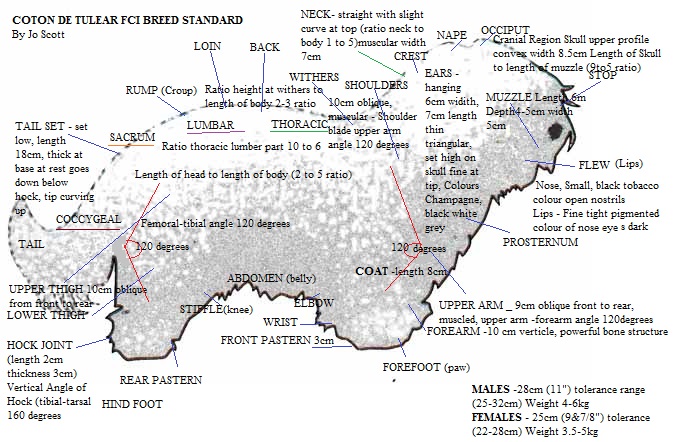
Small dog, suitable for apartment, with long cotton-like coat and round dark, expressive and intelligent eyes.
Important Proportions:
Ratio height at the withers to length of the body = 2 to 3 ratio
Length of the head to length of the body = 2 to 5 ratio
Length of the skull to length of the muzzle = 9 to 5 ratio
Temperament & Behaviour - A little boisterous, merry, a bit of a clown, very loyal to his master
Head - Seen in profile - short, Seen from above - triangular
Cranial Region Skull - Upper profile convex. Width about 8.5 cm (3 3/8")
Supercialiary arches - slightly developed. Slightly frontal furrow.
Occipital protuberance - non existent.
Occipital crest - only slightly perceptible.
Stop - Only slightly accenttuated
Facial Region
Nose - Small, black, dark tobacco colour tolerated. Open nostrils.
Muzzle - About 6 cm (2 3/8") in length, about 4-5 cm (1 3/4") in depth and about 5 cm (2") in width.
Nasal bridge straight
Lower jaw in straight line
Lips - Fine, tight, pigmented as the colour of the nose
Teeth - Perfect, small and white, lower incisors placed just forward, just behind or level with the upper incisors.
Eyes - Round, dark, bright, well set apart, pigmented with colour of the nose, eyelids fine.
Ears - Hanging, about 6 cm (2 3/8") in width, about 7 cm (2 3/4") in length, thin, triangular, set high on the skull. Fine at the tip, bent at the base, covered with white hairs or with tints in the following three possibilities
1 Champagne
2 Mixture of yellow and black hairs
3 mixture of white and black hairs giving the impression of a light grey patch.
Neck
Profile - straight, slightly curved at the top. Ratio neck-body = 1/5.
Length - About 8 cm (3 1/8").
Shape - Bulging, muscular,
Width - About 7 cm (2 3/4").
Skin - Tight
Body (Seen as a whole)
Upper line slightly convex
Withers - Only slightly accentuated, set neck strong
Back & Loins - Very slightly arched, well muscled.
Ratio thoracic lumbar part = 10/6.
Belly & Loins
Round, less broad than the chest, belly hardly tucked up.
Tail
Set low, length about 18 cm (7 1/8") thick at base, fine at the tip, when at rest goes down to below hock with tip curving upwards
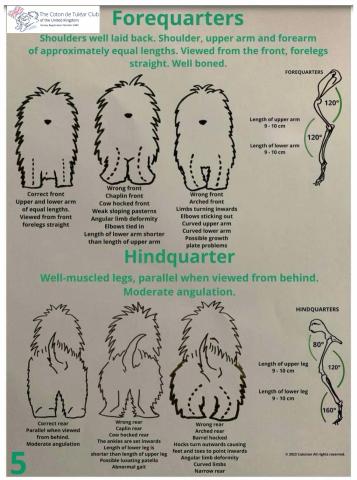
Forequarters (seen as a whole)
Legs vertical seen from the front and in profile
Proportions - 1/1
Shoulders - About 10 cm (4") oblique, muscular.
Upperarm - About 9 cm (3 1/2"), oblique front to rear, muscled.
Shoulder blade upper arm angle - 120 degrees
Forearm - About 10 cm (4"), vertical. Powerful bone structure. Upperarm - forearm angle = 120 degrees.
Pastern joint - About 3 cm (1 1/8").
Pastern - About 3 cm (1 1/8")
Front Feet - About 3 cm (1 1/8"), round shaped, small.
Toes - Tightly closed, well-formed, well-centred and pigmented pads.
Hindquarters (seen as a whole)
Legs vertical seen in profile and from behind.
Proportion - 1/1
Upper thighs - About 10 cm (4"), muscular.
Coaxial-femoral angle - 80 degrees
Lower Thighs - About 10 cm (4"), oblique from front to rear.
Femoral-tibial angle - 120 degrees.
Hock joint - Length about 2 cm (3/4"), thickness about 3 cm (1 /8").
Angle of hook - (tibial-tarsal) 160 degrees
Hock- Length about 7 cm (2 3/4"), Width about 2 cm (3/4"). Vertical position
Hind feet - Round shaped toes with only slight a centuated curve, tightly closed, pads flat and pigmented.
Movement
Walk normal, trot shortened. Preferred pace a trot.
Skin
Fine, well adherent in each part of the body. May be pigmented with grey, more or less dark patches
Hair
Fine, about 8 cm (3 1/8") long, slightly wavy, of coton texture.
Colour - White, a few champagne yellow or grey more or less dark patches, notably on the ears, are tolerated.
Size and weight
Males - 28 cm (11"), tolerance up to 32 cm (12 5/8") maximum and 25 cm (9 7/8") minimum.
Weight - From 4 to 6 kg maximum (8.8 to maximum 13.2 pounds)
Females - 25 cm (9 7/8") tolerance up to 28 cm (11") maximum and 22 cm (8 5/8") minimum.
Weight - From 3.5 to 5 kg maximum (7.7 to maximum 11 pounds).
The weights are proportional in relation to the size but must not exceed the maximum. Example - a male of 11" at the withers should weigh approximately 5 kg (11 pounds), a male of 12 5/8" at the withers should weigh approximately 6 kg (13.2 pounds).
Type
The desirable type is the one described. There are, however, dogs of this breed that are higher on the legs.
Faults
Any department from the foregoing points should be considered a fault and the seriousness with which the fault should be regarded should be in exact proportion to its degree.
Serious Faults
Muzzle - Too small or too thick.
Skull - Flat or too bulging. Stop - Too marked or non-existent.
Nasal bridge - Arched
Teeth - Not regularly aligned (incisors), carious teeth, serious prognathism (more than the thickness of the incisors).
Eyes - Light, set too close, entropion, prominent, vicious look.
Ears - Too short, hairs too short, attachment narrow or too thick, straight.
Back - Saddle back, too long.
Rump - Horizontal, narrow.
Chest - Badly developed.
Neck - Too short or too long, thin.
Tail - Too long, too straight.
Legs - Turned in or out, closed together or loose, too wide apart, barrel hocks or cow-hocks, bad angulation.
Thighs - Insufficient muscle, insufficient hair.
Skin - Wrinkled, thick.
Coat (hair) - Too short, too long, curly, silky texture.
Eliminating faults (disqualification)
Nose with pink spots or patches, too light.
Depigmented lips, pink spotted lips heavy and drooping.
Eyelids white, insufficiently pigmented, pink spots.
Tail rolled up or carried straight like a candle or flagpole, tail-less.
Neck too long
Height and weight over the maximum.
Coat strongly marked with brown or pure black.
N.B. Male animals should have two apparently normal testicles fully descended into the scrotum.
Artemis,. Le coton de Tuléar,
Battaglia, Carmen, L,. 2014. "Do you see what I see?" Canine Chronicle, April pp. 108. Battaglia, Carmen, 2008. "More than meets the eye" Canine Chronicle, Ocala, Fl., pp. 300, 302
Brackett, Lloyd, and Hartwell, 1965. Laurence A., "The Dog in Motion", Dog World Magazine, (USA) August 1961- October 1965
Brkic, Goran,. Le coton de Tuléar,
Carriere, Monique,.The care and the grooming of The Coton De Tuléar,
Cellier, Catherine,. Les Cotons de Tulear d’Ivandry
De Luca, Eli.,Coton’s World
De Vecchi, Brabant-Brkic, Nathalie,. II Coton de tuléar,
De Vecchi, Catala, Raymond, Le coton de tuléar,
Elliot, Rachel Page, 2001. Dog steps, A New Look, Third Edition, Doral Publishing, Sun City, Arizona, pg. 68 -73
Gilbert, Edward M., & Brown, Thelma R., 1995. Structure and Terminology, Howell Book House NY.
Jenkins, Farish A., Jr. "The Movement of the Shoulder in the Claviculate and Aclaviculate Mammals", Department of Biology, Museum of Comparative Zoology, Harvard university, Cambridge, MA
Jespersen, Brigitte,.Grooming and care of the Coton de Tulear.
Jolly, Alison.,Lords and Lemurs: Mad Scientists, Kings with Spears and the Survival of Diversity in Madagascar
Jones, J, Tucker, T., Tan, J., Pierce, B., Foxworth, J, Long, B., Harper, T., Morens, D. 2013. "Improving understanding of early behavioral indicators of lumbosacral disease in working dogs using 3D visualization of skeletal movement during working task: Feasibility study", J. Beh., 8, pp. 309-315.
Knorr,Wolfgang,. 2003. Coton de Tulear
Lyon, McDowell. 1950. Dog in Action, Howell Book House, NY, NY.
Gilbert, E, and Gilbert, P. 2013. Encyclopedia of K-9 Terminology. Dogwise Publications, Wenatchee, WA.
Muss Le Chiens, Carre, Mova,. L'education du Coton de Tuléar,.
Ross, Clark,D. Medical, Genetic & Behavioral Risk Factors of the Coton de Tulear
Russell,Robert Jay. The Official Coton de Tulear Book
Stonewood,M,.The Coton de Tuléar,
Online sources:
Breeding better dogs - www.breeding better dogs.com
The Royal Kennel Club - www.the kennel club.org.uk
The Showsite Magazine special Coton de Tulear edition - http://show sight magazine.com






















